

The scope needed is public_repo for a public repository or repo for a private repository. 1 Answer git remote add origin :User/UserRepo.git git remote set-url origin :User/UserRepo.git git push -u origin master. Use this GitHub guide for creating access tokens. Run the git remote add origin command from your local repository with the -set-upstream and the name of the active branch to push. Obtain the git remote add URL for the remote repository and add credentials if needed.
GIT ADD REMOTE AND PUSH HOW TO
git push is utilized to send the committed changes to remote repositories for collaboration. git/config when you clone a repository and when you add or update remotes to your repository (we cover how to add. This is what the 'origin' remote connection points to. In addition to git add and git commit, a third command git push is essential for a complete collaborative Git workflow. This local Git repository will already have a connection to the original remote set up, automatically. Adding access token to credential store How to Add a Remote in Git Cloning a repository from a remote server downloads the project to your local computer and leaves you with a local Git repository.Configuring build secure variable with access token.We will be using GitHub as a repository provider, however described technique could be applied to any Git hosting.Īt a glance the entire process consists of these steps: To add a new remote, use the git remote add command on the terminal, in the directory your repository is stored at. So, to push your changes to the remote repository, you couldve used.
GIT ADD REMOTE AND PUSH INSTALL
This article will demonstrate how to use Git credential store to avoid Git asking for credentials and stalling the build. The first two things youll want to do are install git and create a free GitHub. The scenario with custom SSH key is described in this article ( with the only difference is that the key should be deployed under GitHub user account, not repo, to have write access). Two methods to access remote Git repository exist: SSH and credentials store. A new repo from scratch Create a directory to contain the project. In most cases you can’t supply username/password in command line ( we are not considering the case when credentials are embedded in repo URL as this is bad). If you try using any Git command against remote repository you’ll get stuck build because Git is asking for credentials. Lets say we have an empty remote repository and we have some code. So you may have to check out the wanted branch: git checkout masterīut the main question here is how to authenticate Git commands. Initialize a repository locally and sync it to the remote repository - Instructor So lets look at a different scenario. Note: AppVeyor checks out only the last commit and not the entire branch. If you still end up with errors like "Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do not have locally", this is normally because that the remote repo is recently created manually.On_success : - git commit. Otherwise you will have to name local branch first by $ git branch -m Īnd then push it to add a new branch called $ git push origin -u
Push the changes in your local repository to GitHub if there is a remote branch called master (or main if that's what you're using) $ git push origin master To push the main repo, you first have to add the remote server to Git by running git remote add$ git commit -m "First commit"Īt the top of your GitHub repository's Quick Setup page, click to copy the remote repository URL. Ĭommit the files that you've staged in your local repository.
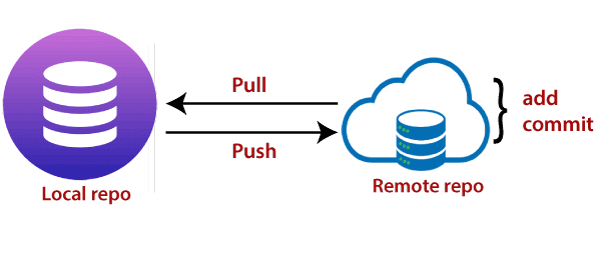
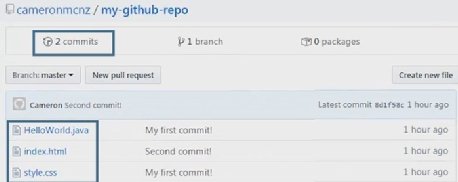
$ git initĪdd the files in your new local repository. Initialize the local directory as a Git repository. Change the current working directory to your local project.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
